Computed Tomography Perfusion and Angiography for Death by Neurologic Criteria
- 이정희
- 2025년 9월 10일
- 4분 분량
et al
2025년06월13일
JAMA Neurol. Published online: June 13, 2025.
DOI:10.1001/jamaneurol.2025.2375
Abstract
Importance Accurate and timely confirmation of death by neurologic criteria (DNC) is essential for clinical decision-making and organ-donation processes, yet currently available ancillary tests have suboptimal diagnostic performance or limited validation.
Objectives To determine the diagnostic accuracy, interrater reliability, and safety of brain computed tomography (CT) perfusion and CT angiography as ancillary investigations for DNC.
Design, Setting, and Participants Between April 25, 2017, and March 10, 2021, a prospective, multicenter, blinded diagnostic accuracy cohort study was conducted in 15 adult intensive care units across Canada. Consecutive, critically ill adults (aged ≥18 years) with a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 3 and no confounding factors who were at high risk of DNC were included. Data collection and analysis were performed from April 2021 to July 2024.
Exposure Contrast-enhanced brain CT perfusion with CT angiography reconstructions performed within 2 hours of a blinded, standardized clinical DNC examination.
Main Outcomes and Measures The primary outcomes were the sensitivity and specificity of qualitative and quantitative brainstem CT perfusion for DNC determination, assessed by 2 independent neuroradiologists blinded to clinical findings; the prespecified validation threshold was greater than 98%. Secondary outcomes were the diagnostic accuracy of whole-brain CT perfusion and CT angiography, interrater reliability (Cohen κ), and adverse events associated with imaging.
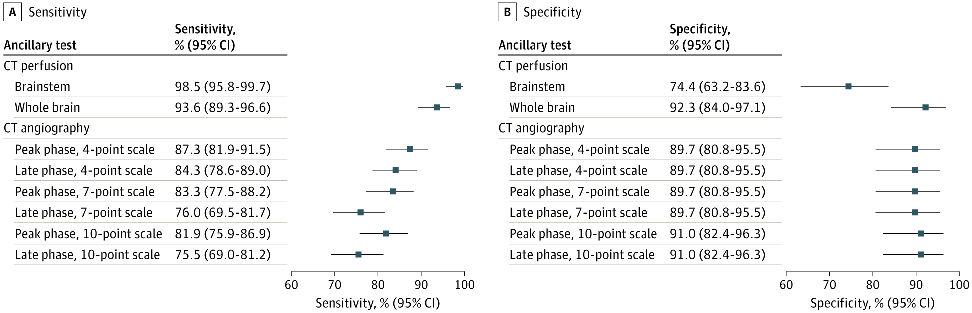
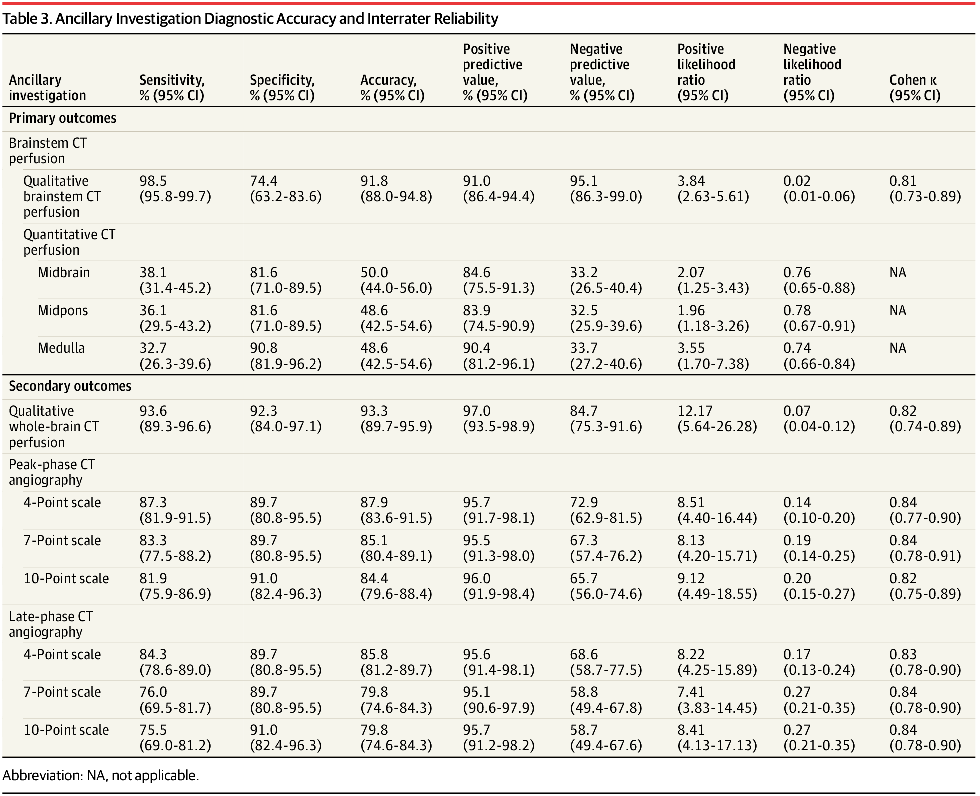
Results A total of 282 patients (mean [SD] age, 57.8 [15.4] years; 133 [47%] female) completed the study protocol and were included in the primary analysis; 204 (72%) of these were ultimately declared deceased by standardized clinical criteria. Qualitative brainstem CT perfusion showed a sensitivity of 98.5% (95% CI, 95.8%-99.7%) and a specificity of 74.4% (95% CI, 63.2%-83.6%); quantitative brainstem CT perfusion was not diagnostically accurate. Qualitative whole-brain CT perfusion yielded a sensitivity of 93.6% (95% CI, 89.3%-96.6%) and a specificity of 92.3% (95% CI, 84.0%-97.1%). CT angiography sensitivity ranged from 75.5% (95% CI, 69.0%-81.2%) to 87.3% (95% CI, 81.9%-91.5%), and its specificity ranged from 89.7% (95% CI, 80.8%-95.5%) to 91.0% (95% CI, 82.4%-96.3%). Interrater reliability was excellent for all ancillary tests (κ ranged from 0.81 [95% CI, 0.73-0.89] to 0.84 [95% CI, 0.78-0.91]). Fourteen patients (5%) experienced minor, self-limited adverse events; no serious adverse events occurred.
Conclusions and Relevance The observed sensitivity and specificity measures for CT perfusion and CT angiography as an ancillary test for DNC did not meet the prespecified validation threshold of greater than 98%. Clinical examination remains the cornerstone of DNC, and ancillary imaging should be interpreted cautiously within a comprehensive clinical assessment.
Key Points
Question In intensive care unit patients at risk of death by neurologic criteria (DNC), what is the diagnostic accuracy of brain computed tomography (CT) perfusion and CT angiography compared with the clinical examination?
Findings In a multicenter diagnostic study of 282 patients (204 with DNC), qualitative brainstem CT perfusion showed 98.5% sensitivity and 74.4% specificity, whole-brain CT perfusion showed 93.6% sensitivity and 92.3% specificity, and CT angiography showed 75.5% to 87.3% sensitivity and 89.7% to 91.0% specificity.
Meaning None of the imaging modalities met the prespecified accuracy threshold of greater than 98%, supporting their role only as ancillary rather than standalone tests for confirming DNC.
요약
· 중요성 : 신경학적 기준에 따른 사망(DNC, death by neurologic criteria)의 정확하고 시기적절한 확인은 임상적 의사결정 및 장기 기증 과정에서 매우 중요하다. 그러나 현재 이용 가능한 보조적 검사(ancillary tests)는 진단 성능이 최적이 아니거나 검증이 제한적이다.
· 목적 : 뇌 컴퓨터단층촬영(CT) 관류 영상(CT perfusion) 및 CT 혈관조영술(CT angiography)을 DNC 보조 검사로 사용할 때, 이들의 진단 정확도(diagnostic accuracy), 평가자 간 신뢰도(interrater reliability) 및 안전성(safety)을 평가하는 것
· 연구 설계, 환경 및 대상자 :
-연구 설계: 전향적, 다기관, 이중맹검 진단 정확도 코호트 연구
-연구 장소: 캐나다 전역 15개 성인 중환자실(ICU)
-연구 기간: 2017년 4월 25일 ~ 2021년 3월 10일
-연구 대상:
▪ 연속적으로 모집된 중증 성인 환자(≥18세)
▪ 글래스고우 혼수척도(GCS) 3점
▪ 혼동요인 없는DNC(신경학적 기준 사망) 고위험군
-자료 수집 및 분석: 2021년 4월 ~ 2024년 7월
· 중재 :
표준화된 임상 뇌사(DNC) 검사 후 2시간 이내에 맹검 상태서 조영증강 CT 관류(CT perfusion) 및 CTA(CT Angiography)를 시행함
· 주요 결과 및 평가지표 :
-주요 평가 지표
▪ 두 명의 신경영상 전문의(neuroradiologists)가 임상 소견을 모른 채(blinded) 평가한 정성적(qualitative) 및 정량적(quantitative) 뇌간 CT 관류의 DNC 진단 민감도(sensitivity) 및 특이도(specificity)
▪ 사전 설정된(validation) 기준: 민감도와 특이도 모두 98% 초과
-부차적 평가 지표
▪ 전뇌 CT 관류(whole-brain CT perfusion)의 진단 정확도
▪ CT 혈관조영술(CTA)의 진단 정확도
▪ 평가자 간 신뢰도(Cohen's κ)
▪ 영상검사 관련 이상반응 발생 여부
· 결과 :
-최종 분석 대상자: 282명
▪ 평균 연령: 57.8세[15.4]
▪ 여성: 133명(47%)
▪ 이 중 204명(72%)은 신경학적 기준 사망(DNC)로 선언됨
-정성적 뇌간 CT 관류:
▪ 민감도 98.5% (95% CI, 95.8%~99.7%)
▪ 특이도 74.4% (95% CI, 63.2%~83.6%)
-정량적 뇌간 CT 관류:
▪ 진단적 정확성이 부족하여 임상적으로 유용하지 않음.
-정성적 전뇌 CT 관류:
▪ 민감도 93.6% (95% CI, 89.3%~96.6%)
▪ 특이도 92.3% (95% CI, 84.0%~97.1%)
-CT 혈관조영술(CTA):
▪ 민감도 75.5% (95% CI, 69.0%~81.2%) ~ 87.3% (95% CI, 81.9%~91.5%)
▪ 특이도 89.7% (95% CI, 80.8%~95.5%) ~ 91.0% (95% CI, 82.4%~96.3%)
-평가자 간 신뢰도
▪ Cohen's κ = 0.81 (95% CI, 0.73%~0.89%) ~ 0.84 (95% CI, 0.78%~ 0.91%)
▪ 매우 우수한 합치도를 보임.
-이상반응
▪ 14명(5%)에서 경미하고 일시적인 이상반응 발생
▪ 심각한 이상반응은 보고되지 않음
· 결론 및 의의 :
신경학적 기준에 따른 사망(DNC) 보조검사로서 CT 관류(CT Perfusion) 및 CT 혈관조영술(CT Angiography)의 민감도 및 특이도는 사전 설정된 검증 기준(>98%)을 충족하지 못함.
따라서, 임상적 신경학적 검사는 여전히 DNC 판단의 핵심(gold standard)이며, 보조적 영상검사는 반드시 종합적 임상 평가의 일부로 신중하게 해석 해야함.




댓글