Lab of Neurologic recovery & Rejuvenation
전한울
2024년 4월 29일
- 본 논문은 소분자 기반으로 특정 단백질의 선택적 분해를 유도하는 Targeted Protein Degradation(TPD) 기술에 대해 설명함. TPD는 **PROTAC(Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras)**와 Molecular Glue Degraders라는 두 주요 기법으로 구분할 수 있음. 이 기술은 기존 접근법으로는 공략할 수 없었던 단백질들을 표적화할 수 있다는 점에서 기존 기법과 차별화 됨.
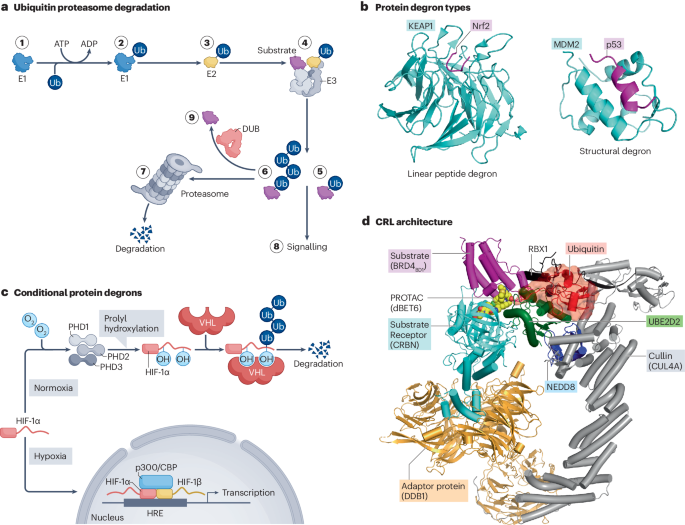
Targeted protein degradation refers to the use of small molecules to induce the selective degradation of proteins. In its most common form, this degradation is achieved through ligand-mediated neo-interactions between ubiquitin E3 ligases — the principal waste disposal machines of a cell — and the protein targets of interest, resulting in ubiquitylation and subsequent proteasomal degradation. Notable advances have been made in biological and mechanistic understanding of serendipitously discovered degraders. This improved understanding and novel chemistry has not only provided clinical proof of concept for targeted protein degradation but has also led to rapid growth of the field, with dozens of investigational drugs in active clinical trials. Two distinct classes of protein degradation therapeutics are being widely explored: bifunctional PROTACs and molecular glue degraders, both of which have their unique advantages and challenges. Here, we review the current landscape of targeted protein degradation approaches and how they have parallels in biological processes. We also outline the ongoing clinical exploration of novel degraders and provide some perspectives on the directions the field might take.