Lab of Neurologic recovery & Rejuvenation
전한울
2024년 9월 28일
- Introduction to TPD:
TPD represents a revolutionary approach to disease management, utilizing the body's natural proteolytic systems (e.g., the ubiquitin-proteasome system and lysosomal pathways) to degrade disease-causing proteins selectively.
Unlike traditional inhibitors, TPD offers the potential to address "undruggable" proteins and reduce off-target effects and drug resistance.
Key Mechanisms:
Proteolysis-Targeting Chimeras (PROTACs) and Molecular Glues (MGs) are two primary TPD approaches.
PROTACs form ternary complexes to recruit E3 ligases for targeted protein ubiquitination and degradation.
MGs induce or stabilize protein-protein interactions to promote degradation via E3 ligases.
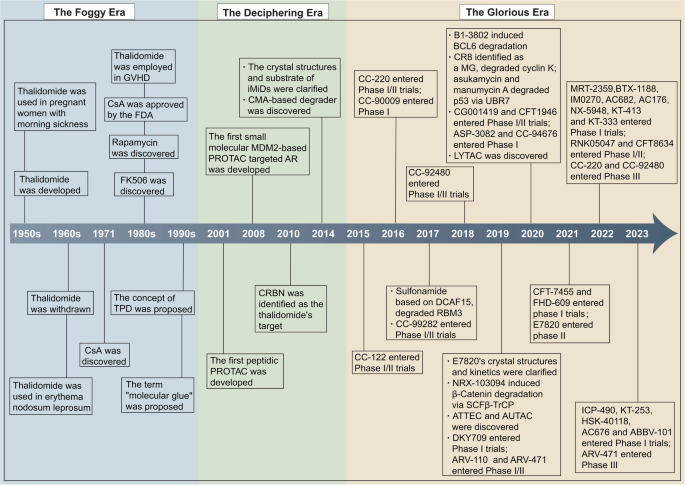
Targeted protein degradation (TPD) represents a revolutionary therapeutic strategy in disease management, providing a stark contrast to traditional therapeutic approaches like small molecule inhibitors that primarily focus on inhibiting protein function. This advanced technology capitalizes on the cell’s intrinsic proteolytic systems, including the proteasome and lysosomal pathways, to selectively eliminate disease-causing proteins. TPD not only enhances the efficacy of treatments but also expands the scope of protein degradation applications. Despite its considerable potential, TPD faces challenges related to the properties of the drugs and their rational design. This review thoroughly explores the mechanisms and clinical advancements of TPD, from its initial conceptualization to practical implementation, with a particular focus on proteolysis-targeting chimeras and molecular glues. In addition, the review delves into emerging technologies and methodologies aimed at addressing these challenges and enhancing therapeutic efficacy. We also discuss the significant clinical trials and highlight the promising therapeutic outcomes associated with TPD drugs, illustrating their potential to transform the treatment landscape. Furthermore, the review considers the benefits of combining TPD with other therapies to enhance overall treatment effectiveness and overcome drug resistance. The future directions of TPD applications are also explored, presenting an optimistic perspective on further innovations. By offering a comprehensive overview of the current innovations and the challenges faced, this review assesses the transformative potential of TPD in revolutionizing drug development and disease management, setting the stage for a new era in medical therapy.